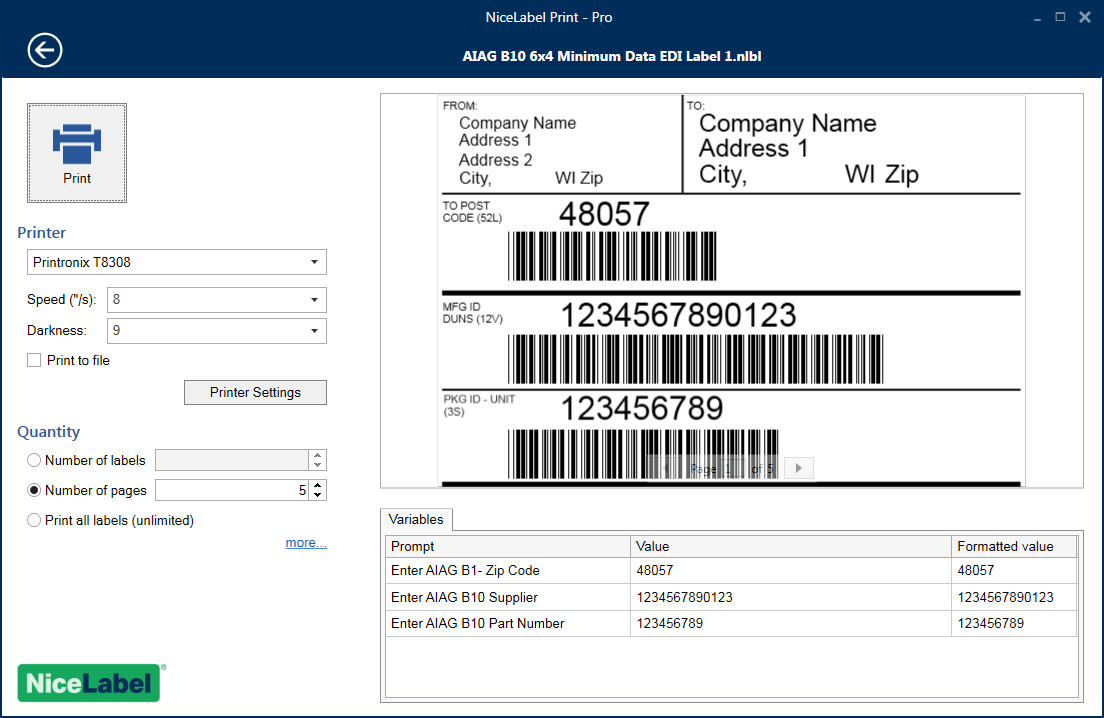
Creating labels for logistics and inserting data into print fields
In addition to printing labels, we are also involved in the labelling of goods. Since we often get questions about this topic and it is very broad, we decided to make it into a short series. We will present information covering the production, printing, and application of labels. We'll go over printing options, technologies, materials, surface treatment, quality, and durability. In the following text we describe how to create labels for logistics, and how to insert data into print fields.
WHAT IS MOST OFTEN PRINTED
It is always up to the customer to decide what level of details is needed to print. It is possible to print on the entire surface of the label, or to print only the production and expiry date, serial number, barcode, etc.. This can be divided into two fields, logistics and other applications.
In logistics we print a full range of data, text, barcodes, and 2D codes usually on the entire surface of the
labels in designated fields. We can use "fixed" and "variable", or combine the printing of fixed data entered in the application with variable data entered from a database or a customer’s system.
Data, text, barcode and other information are inserted on the label surface using an application designed for print creation. We use and provide our customers with NiceLabel and BarTender.

Customers create print fields in the application, which are placed on the label as they chose. Then fixed or variable data are inserted (texts, barcodes...), from databases or the system.
THE APPLICATION has tools to easliy insert and configure linear and 2D codes,images, symbols, etc..
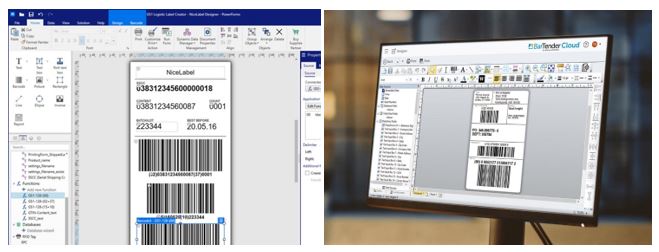
FIXED, PERMANENT DATA ON LABELS
Fixed data usually contains information about the product as required by legislation, e.g. name, composition, allergens, recycling symbols, or registered barcodes. Labels with this information are usually placed on the back or bottom of the product. This data can also be reprinted in the graphic label field.


VARIABLE DATA:
For variable data, customers create print fields in the same way as for creating a label with fixed data. Data is then automatically inserted into these fields from a specified location, for example, time and date fields are typically inserted from the PC operating system. Data can be entered from databases or a customer's production system.

Next time, we will look at technologies and methods of reprinting data on labels, followed by information about materials suitable for printing and their surface treatment.